The Structure of the Milky Way

| H. E. Smith | Winter 2007 |

|
|
Physics 7 - Lecture Summary #13 The Structure of the Milky Way |
 |

 |
The
Milky Way system is a spiral galaxy consisting of over 400 billion stars , plus gas and dust arranged into three general components as shown to the left:
|
The Halo
The Halo consists of the oldest stars known, including about 146
Globular Clusters,
believed to have been formed during the early formation of the Galaxy with
ages of 10-15 billion years from their H-R
Diagrams. The halo is also filled with a very diffuse, hot,
highly-ionized gas. The very hot gas in the halo produces a
gamma-ray
halo.
Neither the full extent nor the mass of the halo is well known.
Investigations of the gaseous halos of other spiral galaxies show that the
gas in the halo extends much further than previously thought, out to hundreds
of thousands of light years. Studies of the rotation of the Milky Way show
that the halo dominates the mass of the galaxy, but the material is not
visible, now called dark matter.
The Disk
The disk of the Galaxy is a flattened, rotating system which contains the Sun
and other intermediate-to-young stars. The sun sits about 2/3 of the way from
the center to the edge of the disk (about 25,000l.y. by the most modern
estimates). The sun revolves
around the center of the galaxy about once every 250 million years. The disk
also the galaxy about contains atomic (HI) and molecular (H2) gas
and dust.
Here is an excellent tutorial on the
Shape of the
Milky Way by Rick Arendt.
The Optical View
(above) is dominated by emission from stars and extinction by
dust; we can see only a thousand light years
or so in the plane. The infrared views from IRAS, shown below demonstrate
that the shape of the Milky Way is more regular
Stars in the Milky Way at Mid-Infrared Wavelengths (free from dust extinction -
NASA/IRAS Image).

Credit & Copyright:
John P. Gleason,
Celestial Images

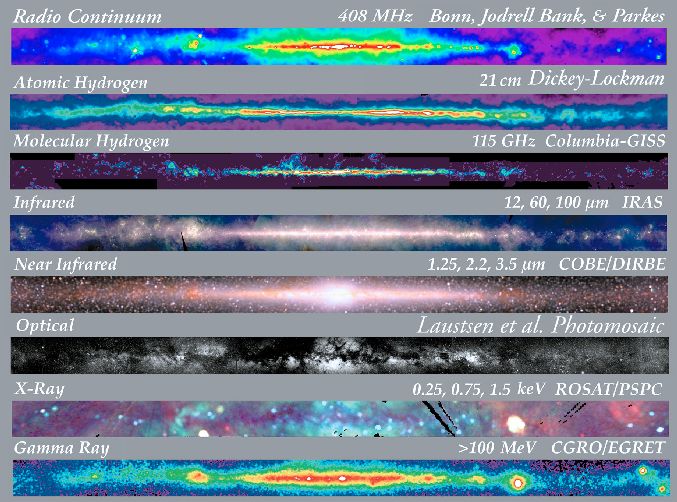
Multiwavelength Milky Way
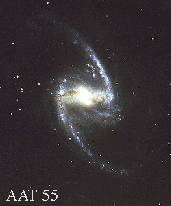 |
Since the Earth lies in the disk of the Milky Way, dust prevents us from determining the large scale structure of the Galaxy's spiral pattern beyond a few thousand light-years. Radio observations have detailed the structure of the gas in the spiral arms, but it is still not known if our galaxy is a normal spiral like our neighbor Andromeda, or a barred spiral like shown to the left. The bulge of the galaxy is slightly elongated in the direction of the Sun, which may be due to a bar. |
The Center of the Galaxy
What lies at the
center of our Galaxy? Again, dust obscures the visible light
from us and we must use radio and infrared observations to elicit the nuclear
properties of the Galaxy. A census shows us that the Galactic Center region
is an unusually crowded place, even in this visible-light
Map of Central region. At radio wavelengths, where we can peer down to the
very center, we see the complex strctures shown in the
1-meter wavelength radio
map made by NRL astronomers which is shown below. The map shows a region
about 2000 light-years on a side; the center of the Milky Way coincides with
the source marked Sag A (or Sagittarius A), which is actually three sources,
a yound supernova remnant on the east side, an unusual ionized hydrogen region
on the west side, and a very compact source called Sagittarius A* at the very
center.
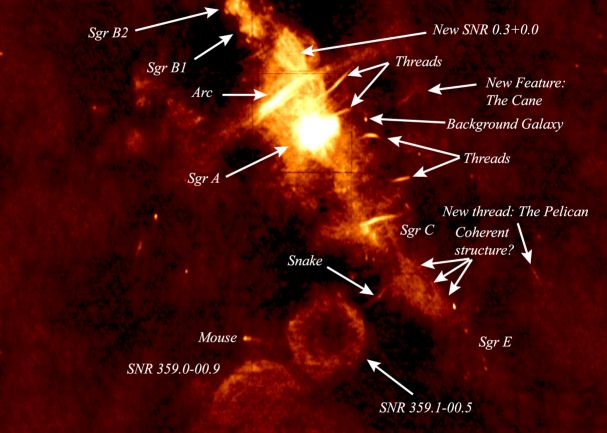 Radio image of the central region of the Milky Way |
Although there is no lack of fascinating questions about the Galactic Center, recent interest has been focused on the question of the possibility that a massive black hole exists at the center of the central star cluster. The presence of very high velocities in the stars and gas near the center of the galaxy has suggested to astronomers for a long time that a massive black hole might be present, providing a strong enough gravitational pull to keep the stars and gas in orbit. Andrea Ghez, a professor at UCLA, used the Keck 10-meter telescope at infrared wavelengths to measure the velocities of 20 stars that lie close to the galactic center over a three-year period. She found the stars are orbiting at speeds up to 1000 km/s (3 million miles per hour)! Observation done by scientists at the Max-Planck Institut in Germany have confirmed these results. This large gravitational acceleration requires an object with a mass 2.5 million times that of our Sun.
The stars are located near Sagittarius A*, the radio source lying near the center of the galaxy. From its radio signal alone, Sgr A* did not have to be particularly massive, since its emission is not very powerful. Using the VLBA (Very Long Baseline Array) radio telescope, astronomers studied the motion of Sgr A*; they found a velocity of less than 20 km/sec for Sgr A* itself. This means it is very unlikely that Sgr A* is a single star or group of stars. Only a very massive object could remain stationary under the conditions exisiting at the center of the galaxy. The evidence is mounting that Sag A* is indeed a black hole of 2-3 million times the mass of the sun. Astronomers speculate that the Black Hole is being "fed" by gas from the molecular ring, or supernova remnant. By consuming less than about 1% of the mass of a star each year, releasing gravitational potential energy, Sag A* can easily account for the high-energy phenomena near the galactic center.

![]() The Interstellar Medium
The Interstellar Medium
![]() GR & Black Holes
GR & Black Holes
![]() Physics 7 Lectures
Physics 7 Lectures
![]() Physics 7 Home
Physics 7 Home
Conducted by Gene Smith, CASS/UCSD.
Comments?
You may send email to hsmith@ucsd.edu
Prof. H. E. (Gene) Smith
CASS 0424 UCSD
9500 Gilman Drive
La Jolla, CA 92093-0424
Last updated: 25 February 2001