Clusters of Galaxies


| CASS Astronomy Tutorial Clusters of Galaxies |
 |

 |
Most galaxies are found in gravitationally-bound groups called "clusters". Clusters can be rich, with several thousand galaxies, or poor, with only 20 or 30 members. The Local Group, the cluster to which our own Milky Way galaxy belongs, is made up of about 30 galaxies. |
Clusters of galaxies are classified by their properties;richness (number of members),shape (spherical,flattened, or irregular),and galactic content (spiral-rich,spiral-poor, or elliptical-rich),for example. Some are strong radio sources, while others emit x-rays. The richest nearby cluster is Virgo, 60 million light years from the Milky Way. It contains about 2500 galaxies, mostly ellipticals.
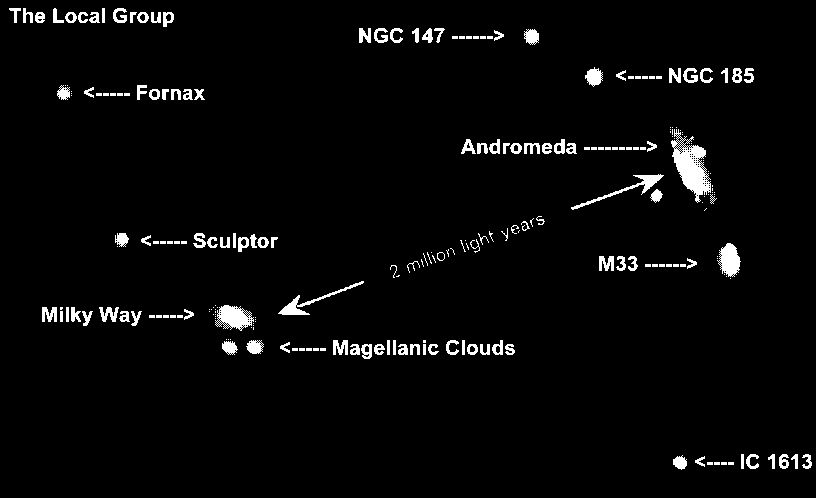
We reside in a small group called the
Local
Group which is dominated by
two giant spiral galaxies, Andromeda and our own Milky Way. In addition to
Messier 33, an intermediate mass Sc galaxy, there are 15 ellipticals and 13
irregular galaxies in the cluster, including the Magellanic Clouds, our
Galaxy's satellites, Messier 32 and NGC 205, satellites of Andromeda. The
group has a size of about 3 million l.y., and has a total mass
of 5 x 1012M
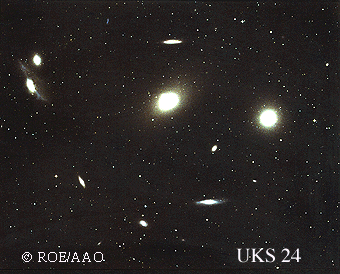
The Virgo Cluster, about 50 million l.y. away, is the nearest regular cluster of galaxies with several hundred members. Our Local Group is an outlying member of a "supercluster" of galaxies of which the Virgo Cluster is the dominant member.
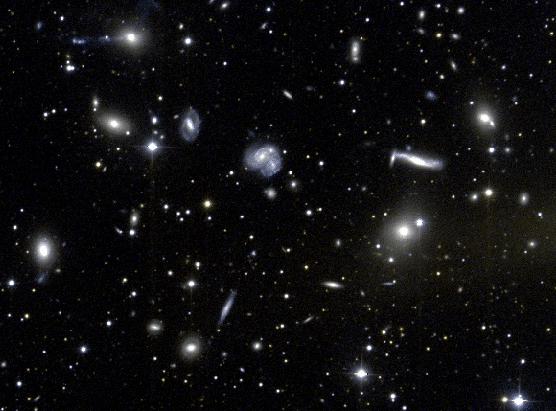

The Hubble Space Telescope has provided the first opportunity to look back into the early universe at clusters. Billions of years ago, clusters contained many more spiral galaxies than they do today. They were probably disrupted over time by collisions and mergers within the clusters.

CL 0024+1654 is a large cluster of galaxies located 5 billion light-years
from Earth. It is distinctive because of its richness (large number
of member galaxies), and its magnificent . The blue loops
in the foreground are lensed images of a spiral galaxy located behind
the cluster.
Cluster Links
Gamma-Ray Bursts
Gamma-Ray Bursts are turning out to be one of the most explosive new areas of astronomical research. Gamma-ray bursts were discovered in 1967 by the Vela Satellites launched to monitor compliance with the 1963 Nuclear Test-Ban Treaty by detecting gamma-rays from atmospheric nuclear tests. Fortunately, it was quickly established that the bursts are of extraterrestrial origin (no, not ET!) rather than some rogue state initiating nuclear war. Initially the number of bursts was too small and the ability to pinpoint the bursts too poor to determine their origin.
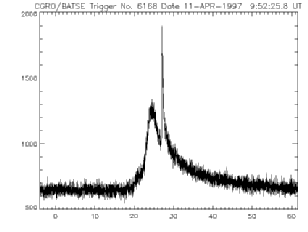 Gamma-ray burst observed by BATSE | In 1991 the Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory carried its Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE), built with participation by UCSD's high energy astrophysicists. into orbit. The gamma-ray bursts last from a few seconds to a couple of minutes and, until very recently, were undetected at other wavelengths. BATSE has observed a couple thousand bursts and determined that they are distributed uniformly around the sky. |

Gamma Ray Burst Links

![]() Quasars & AGN
Quasars & AGN
![]() Galaxies
Galaxies
![]() Outreach & Education
Outreach & Education
![]() CASS Home
CASS Home
Conducted by Gene Smith, CASS/UCSD.
Comments?
Gene
Smith
Prof. H. E. (Gene) Smith
CASS 0424 UCSD
9500 Gilman Drive
La Jolla, CA 92093-0424
Last updated: 26 April 1999