- 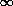 . Since the structure of
almost everyting in our world is electromagnetic in nature; virtually
every phenomenon that is not identifiably nuclear or gravitational is
electromagnetic in nature.
. Since the structure of
almost everyting in our world is electromagnetic in nature; virtually
every phenomenon that is not identifiably nuclear or gravitational is
electromagnetic in nature.
Metal spheres A and B, standing on insulated supports, are initially in
contact with each other. Sphere C, which has a large negative charge is
placed near the other spheres as shown below. While C is nearby, B is moved
to the right so that the two spheres are now separated, then C is removed.
- A & B are now charged. Draw a diagram of the charge distribution on
each sphere with charge sign indicated. Draw in the E-field lines between the
spheres.
- If B is moved toward A, a spark is likely to jump between the spheres
before they come in contact. Explain why. Where did the energy (work) for
this process originate.
- When C is near A & B, positive charges are pulled toward C and
negative charges are repulsed, resulting in a net (induced) positive charge
on A and negative charge on B.
- When A is separated from B, and when C is removed, work is done on the
system. There will be an electrical field between A & B whose strength
depends upon the magnitude of the induced charge and the separation of the
spheres. As A & B are moved toward each other again the field increases
until it exceeds the breakdown field necessary to ionize the air
between the spheres and allow charges to jump from one sphere to another
- a spark - which will reduce the magnitude of the field.
A and B shown below are stars, of equal mass, in a binary star system.
Points 1 - 5 represent small equal test masses. Draw the two forces,
FA &
FB on each point mass, indicating the magnitude of the force by
the length of the vector. Draw the resultant vector at each point with
a different colored pen.
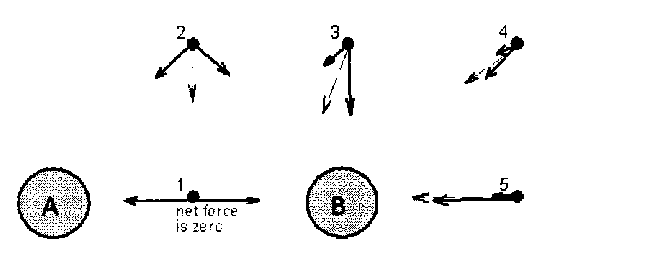 A and B shown above are spherical charges of equal magnitude but
opposite sign.
Draw the electric fields due to the two charges,
EA &
EB at each point, indicating the magnitude of the field by
the length of the vector. Draw the resultant vector at each point with
a different colored pen.
In the diagram for 3 above, suppose A is positive and B is negative. Vectors
for field due to A will point away from A.
A and B shown above are spherical charges of equal magnitude but
opposite sign.
Draw the electric fields due to the two charges,
EA &
EB at each point, indicating the magnitude of the field by
the length of the vector. Draw the resultant vector at each point with
a different colored pen.
In the diagram for 3 above, suppose A is positive and B is negative. Vectors
for field due to A will point away from A.
Two concentric spherical conducting shells A & B
(RA < RB) are charged with charges +Q and -Q
respectively. Determine the Elictric Field for a) r < RA,
b) RA < r < RB, c) r > rA.
Draw a diagram for the E-fields.


 . Since the structure of
almost everyting in our world is electromagnetic in nature; virtually
every phenomenon that is not identifiably nuclear or gravitational is
electromagnetic in nature.
. Since the structure of
almost everyting in our world is electromagnetic in nature; virtually
every phenomenon that is not identifiably nuclear or gravitational is
electromagnetic in nature.
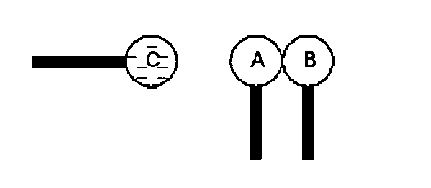
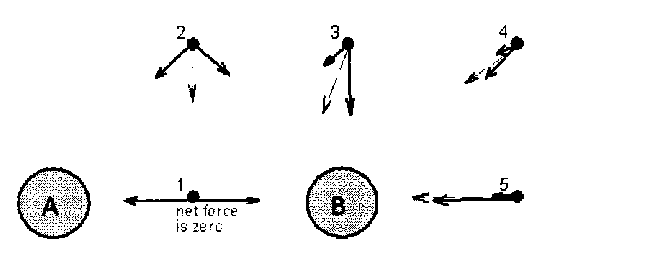

 0 r2 - (RA < r < RB).
See Hecht, p. AN-10 for a more complete explanation.
0 r2 - (RA < r < RB).
See Hecht, p. AN-10 for a more complete explanation.

![]() Physics 1B Home
Physics 1B Home
![]() Tutorials
Tutorials
![]() Tutorial #3
Tutorial #3
![]() Tutorial #5
Tutorial #5